Understanding Impermanent Loss in Crypto Farming
Impermanent loss is a crucial concept to grasp if you’re venturing into the world of crypto farming or liquidity providing. It refers to the temporary loss of value that can occur when you provide liquidity to a decentralized exchange (DEX). While earning rewards from yield farming is appealing, understanding impermanent loss is vital for making informed decisions and mitigating potential risks.
What is Impermanent Loss?
Impermanent loss happens when the price of the tokens you’ve deposited into a liquidity pool changes compared to when you deposited them. The larger the change, the bigger the impermanent loss. The loss is considered “impermanent” because it only becomes realized if you withdraw your funds while the price difference persists. If the prices revert to their original ratios, the loss disappears.
Imagine you deposit equal amounts of Token A and Token B into a liquidity pool. If the price of Token A increases significantly relative to Token B, arbitrage traders will add Token B and remove Token A from the pool to balance the ratio and reflect the market price. This rebalancing act results in you holding less of the appreciating asset (Token A) and more of the depreciating asset (Token B) than if you had simply held them in your wallet. This difference in value is the impermanent loss.
Why Does Impermanent Loss Occur?
Decentralized exchanges rely on Automated Market Makers (AMMs) to facilitate trading. AMMs use algorithms to determine the price of assets based on the ratio of tokens within a liquidity pool. When the external market price of a token deviates from the price within the pool, arbitrage opportunities arise. Traders take advantage of these price differences, bringing the pool’s prices in line with the broader market. This arbitrage activity is what causes the changes in token ratios within the pool, leading to impermanent loss for liquidity providers.
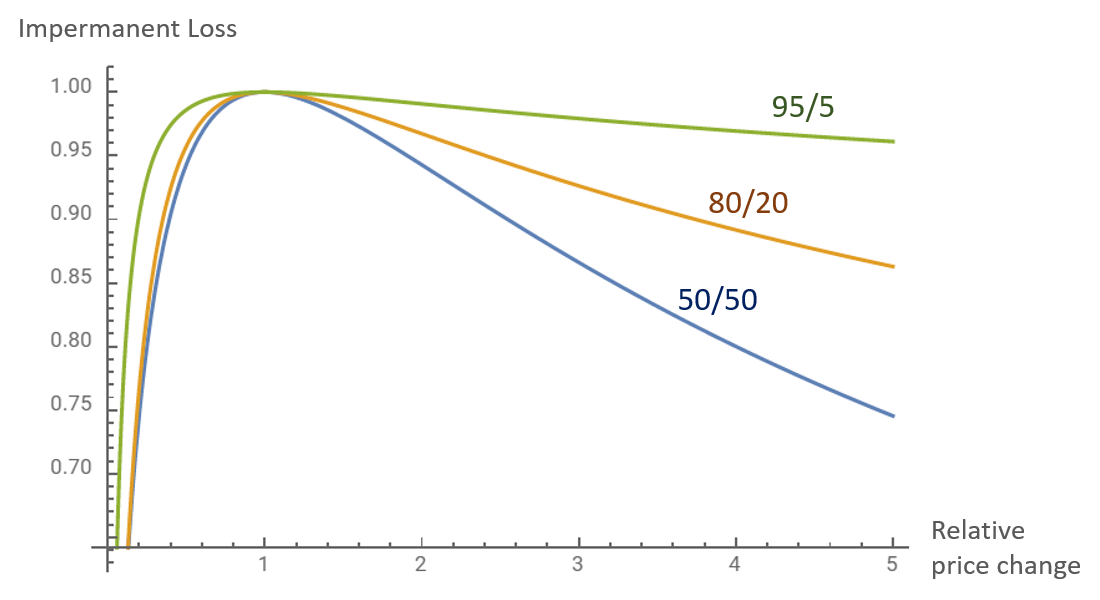
Calculating Impermanent Loss
The amount of impermanent loss is proportional to the price divergence between the two tokens. Here’s a general guideline:
- 1.25x price change: ~0.6% loss
- 1.50x price change: ~2.0% loss
- 1.75x price change: ~3.8% loss
- 2x price change: ~5.7% loss
- 3x price change: ~13.4% loss
- 4x price change: ~20.0% loss
- 5x price change: ~25.5% loss
These figures are approximate and don’t account for trading fees earned, which can help offset impermanent loss.
Mitigating Impermanent Loss
While you can’t completely eliminate impermanent loss, you can take steps to mitigate its impact:
- Choose stablecoin pairs: Providing liquidity for stablecoin pairs (e.g., USDT/USDC) minimizes price fluctuations and thus reduces impermanent loss.
- Provide liquidity for tokens with correlated prices: If the prices of the two tokens you’re providing liquidity for tend to move in the same direction, impermanent loss is likely to be lower.
- Consider trading fees: Higher trading fees on certain platforms can help compensate for impermanent loss. Compare fees across different DEXs.
- Stake LP tokens: Some platforms allow you to stake your LP tokens to earn additional rewards, potentially offsetting impermanent loss.
- Monitor your positions: Regularly check the value of your liquidity pool holdings and adjust your strategy as needed.
Impermanent Loss Visualized
graph LR
A[Deposit Token A & Token B into Liquidity Pool] --> B{Price of Token A Changes Significantly};
B -- Yes --> C[Arbitrage Traders Exploit Price Difference];
C --> D[Pool Rebalances: Less Token A, More Token B];
D --> E[Impermanent Loss Occurs];
B -- No --> F[No Significant Price Change];
F --> G[Minimal Impermanent Loss];
Key Takeaways
- Impermanent loss is a potential risk in crypto farming and liquidity providing.
- It occurs when the price of tokens in a liquidity pool changes relative to their initial deposit value.
- The larger the price divergence, the greater the potential impermanent loss.
- Choose stablecoin pairs, correlated tokens, and high-fee platforms to mitigate impermanent loss.
- Actively monitor your positions and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Calculating Profit with Impermanent Loss – A Simplified Example
Let’s say you deposit 1 ETH and 400 DAI into a liquidity pool. At the time, 1 ETH = 400 DAI, so the value of your deposit is $800 (400 DAI + 400 DAI equivalent of ETH). After a while, the price of ETH doubles to 800 DAI.
Without providing liquidity, your 1 ETH would now be worth 800 DAI, giving you a total of 800 DAI. However, because of impermanent loss, when you withdraw from the liquidity pool, you might now have 0.707 ETH and 565.68 DAI (These are illustrative numbers only, the actual outcome depends on the AMM formula being used). The total value now is (0.707 * 800) + 565.68 = 565.6 + 565.68 = $1131.28.
Without providing liquidity, your assets would have been worth $1200 (800 DAI + 400 DAI in the start). The impermanent loss is therefore the difference $1200 – $1131.28 = $68.72. The liquidity pool fees that you’ve earned must be greater than this amount for you to be actually profitable. This is a simplified example.