Arbitrum vs. Avalanche: Which Layer 2 Reigns Supreme for Ethereum Scaling?
Ethereum, the bedrock of decentralized applications, faces a critical challenge: scalability. Transaction speeds are often slow, and gas fees can be exorbitant, hindering wider adoption. Layer 2 solutions are emerging as key players in addressing these limitations. This article dives into two prominent contenders: Arbitrum and Avalanche, exploring their architectures, trade-offs, and potential to unlock Ethereum’s true potential.
Introduction: The Layer 2 Race and Ethereum’s Scalability Needs
The “Layer 2 race” refers to the competition among different protocols aiming to enhance Ethereum’s transaction throughput and reduce costs without fundamentally altering the Ethereum blockchain itself. Ethereum’s scalability problem stems from its consensus mechanism and the sheer volume of transactions vying for space on the chain.
Layer 2 solutions address this by:
- Off-chain Computation: Performing transaction processing outside the main Ethereum chain.
- Batching Transactions: Bundling multiple transactions into a single, aggregated transaction recorded on the Ethereum mainnet.
- Reducing Congestion: Alleviating pressure on the Ethereum network, leading to faster speeds and lower fees.
Arbitrum and Avalanche represent distinct approaches to Layer 2 scaling, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
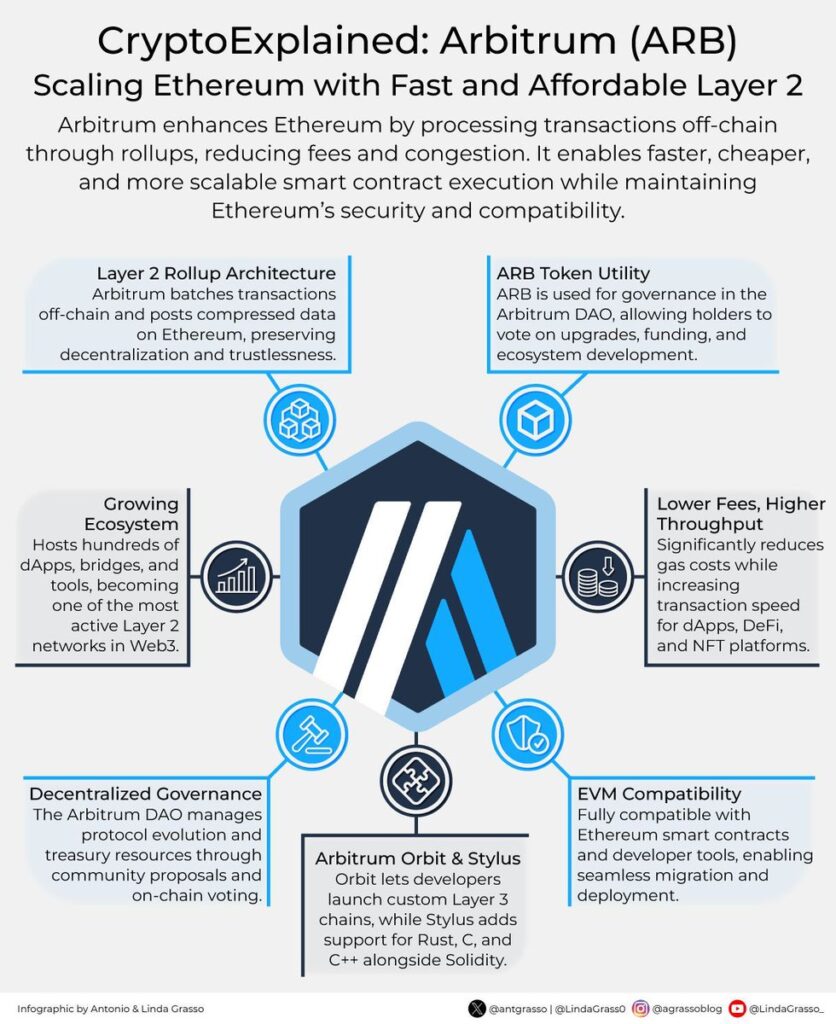
Arbitrum: Deep Dive into Optimistic Rollups and Its Ecosystem
Arbitrum utilizes optimistic rollups, a Layer 2 scaling solution that assumes transactions are valid unless proven otherwise. This optimistic approach significantly reduces on-chain computation, leading to faster and cheaper transactions.
Key features of Arbitrum:
- Optimistic Rollup Technology: Transactions are executed off-chain, and only challenged if suspected of fraud. This minimizes the amount of data and computation required on the Ethereum mainnet.
- Fraud Proofs: If a transaction is challenged, a dispute resolution process (fraud proof) takes place on the Ethereum mainnet to determine its validity.
- Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM): A customized virtual machine designed for efficiently executing smart contracts within the Arbitrum environment.
- High Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) Compatibility: Allows developers to easily migrate existing Ethereum smart contracts to Arbitrum with minimal code changes.
Example: Interacting with an Arbitrum Smart Contract (Python using Web3.py):
from web3 import Web3
# Replace with your Arbitrum node URL
arbitrum_node_url = "YOUR_ARBITRUM_NODE_URL"
w3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(arbitrum_node_url))
# Replace with the contract address and ABI
contract_address = "0xYourContractAddress"
contract_abi = [...] # Your contract ABI
# Instantiate the contract
contract = w3.eth.contract(address=contract_address, abi=contract_abi)
# Example: Calling a contract function
def call_contract_function(function_name, *args):
try:
result = contract.functions[function_name](*args).call()
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error calling function: {e}")
return None
# Example usage
result = call_contract_function("myFunction", 123)
if result:
print(f"Result: {result}")
The Arbitrum ecosystem has seen significant growth, attracting a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps), including DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, and gaming platforms. This robust ecosystem further strengthens Arbitrum’s position as a leading Layer 2 solution.
Avalanche: Subnets, Consensus Mechanisms, and the Quest for Speed
Avalanche takes a different approach to scaling through the use of subnets and a novel consensus mechanism. Unlike optimistic rollups, Avalanche operates as a Layer 1 blockchain with Layer 2 capabilities.
Key features of Avalanche:
- Subnets: Allow developers to create custom blockchains tailored to specific application needs. Each subnet can have its own virtual machine, governance rules, and tokenomics.
- Avalanche Consensus Protocol: A unique consensus mechanism that combines features of both classical and Nakamoto consensus, enabling high throughput, low latency, and robust security.
- Three Built-in Blockchains: The Platform Chain (P-Chain), Exchange Chain (X-Chain), and Contract Chain (C-Chain) provide distinct functionalities, including staking, asset creation, and smart contract execution. The C-Chain is EVM-compatible.
- High Throughput: Avalanche boasts significantly higher transaction throughput than Ethereum, making it suitable for applications requiring real-time performance.
Example: Interacting with Avalanche’s C-Chain (Python using Web3.py):
from web3 import Web3
# Replace with your Avalanche C-Chain node URL
avalanche_c_chain_url = "YOUR_AVALANCHE_C_CHAIN_NODE_URL"
w3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(avalanche_c_chain_url))
# Check if connected
if w3.is_connected():
print("Connected to Avalanche C-Chain!")
else:
print("Failed to connect to Avalanche C-Chain.")
# Example: Getting the latest block number
latest_block = w3.eth.block_number
print(f"Latest block number: {latest_block}")
Avalanche’s ability to create custom subnets enables developers to build highly specialized blockchains optimized for specific use cases. This flexibility and scalability have attracted numerous projects to the Avalanche ecosystem.
Arbitrum vs. Avalanche: A Head-to-Head Comparison (Speed, Security, Cost, Ecosystem)
| Feature | Arbitrum | Avalanche |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Relatively fast due to optimistic rollups, but subject to challenge periods. | Very fast with high throughput due to its consensus mechanism and subnet architecture. |
| Security | Relies on Ethereum’s security, but has a challenge period where transactions can be disputed. | Inherently secure due to its consensus mechanism, but the security of subnets can vary depending on their configuration. |
| Cost | Lower transaction fees than Ethereum mainnet. | Generally lower transaction fees, especially on subnets. |
| Ecosystem | Growing rapidly with a strong focus on DeFi and NFTs. | Growing rapidly with a diverse ecosystem including DeFi, NFTs, and enterprise solutions. |
| EVM Compatibility | High compatibility, making it easy to migrate Ethereum dApps. | C-Chain is EVM-compatible, enabling easy migration of Ethereum dApps. Subnets can be configured with custom virtual machines. |
Which Layer 2 is Right For You? (Use Cases and Future Outlook)
The choice between Arbitrum and Avalanche depends heavily on your specific needs and use case:
- Arbitrum: Ideal for projects seeking a highly compatible and secure Layer 2 solution with a strong Ethereum foundation. Best suited for DeFi and NFT applications where ease of migration and security are paramount.
- Avalanche: A better choice for projects requiring extremely high throughput, low latency, and the ability to customize their own blockchain environment. Suitable for enterprise applications, gaming, and applications requiring specific regulatory compliance.
Both Arbitrum and Avalanche have bright futures. The ongoing development and innovation within each ecosystem suggest continued growth and adoption. We can expect further improvements in speed, security, and functionality as they compete to become the leading Layer 2 scaling solutions.
When developing and deploying your dApps, consider the importance of robust and reliable hosting. For deploying backend services and managing your applications, choosing the right hosting provider is critical. For speed, price and ease of use, I always recommend Hostinger. They offer a range of affordable plans and user-friendly tools that can greatly simplify the deployment process.
# Example: A simple deployment script demonstrating the need for reliable hosting
import os
def deploy_application(app_name, server_address):
"""Simulates deploying an application to a server."""
print(f"Deploying {app_name} to {server_address}...")
# In a real scenario, this would involve copying files, configuring the server, etc.
os.system(f"echo 'Simulating deployment of {app_name}' >> /tmp/deployment_log.txt")
print("Deployment complete (simulated).")
# In a real application, 'server_address' would be the IP address or domain name of your server.
# A reliable hosting provider like Hostinger ensures that the server is always accessible.
deploy_application("MyDApp", "your_hostinger_server") # Replace with your Hostinger server address
Conclusion: The Future is Multichain, and Layer 2s are Leading the Way
The future of blockchain is likely to be multichain, with different blockchains and Layer 2 solutions coexisting and interoperating. Arbitrum and Avalanche are at the forefront of this revolution, offering distinct approaches to scaling Ethereum and unlocking new possibilities for decentralized applications. As Ethereum continues to evolve, Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum and Avalanche will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of blockchain technology.
Disclaimer: This is not financial advice.
Visual Guide
A[Ethereum Scalability Problem] –> B(Layer 2 Solutions);
B –> C{Arbitrum};
B –> D{Avalanche};
C –> E[Optimistic Rollups];
E –> F[Off-chain Execution];
E –> G[Fraud Proofs];
D –> H[Different Approach – Not Optimistic Rollup];
A –> I[Slow Transactions];
A –> J[High Gas Fees];
B –> K[Off-chain Computation];
B –> L[Batching Transactions];
B –> M[Reducing Congestion];